There are many Ear, Nose and Throat practices that see mostly adult patients. Because they don’t see a volume of pediatric ENT patients, the physicians are often reluctant to add OtoAcoustic Emissions (OAE) to their standard audiology battery.This article presents the rational for including OAE as an integral component of the standard audiology test battery ordered for all ear and hearing patients.
When a patient presents with a symptom involving the ear and/or hearing, most audiology clinics will proceed with a standard battery of tests which includes a pure tone air and bone conduction audiogram (with masking as needed), speech reception thresholds, speech discrimination scores and tympanometry with acoustic reflexes. This provides the clinician with valuable information about the patient’s hearing acuity for tones and speech as well as their ability to understand speech and the condition of the middle ear. With these findings along with the results of the otoscopic examination and the details of the patient’s history, the providers will have much of the information they need to proceed with a reasonable treatment path.
OtoAcoustic Emissions (OAE) is a quick and simple test that does not require the participation of the patient. A small probe is simply placed in the ear canal and the test runs automatically in less than one minute for both ears. The OAE response is the result of the motility of the outer hair cells within the cochlear. This is why OAEs are cochlear-specific. The presence of a normal OAE at a particular frequency is consistent with a normal hearing threshold at that frequency. Distortion Product OtoAcoustic Emissions (DPOAE) can be tested clinically from 500 Hz through 10,000 Hz with typical commercially available instrumentation.
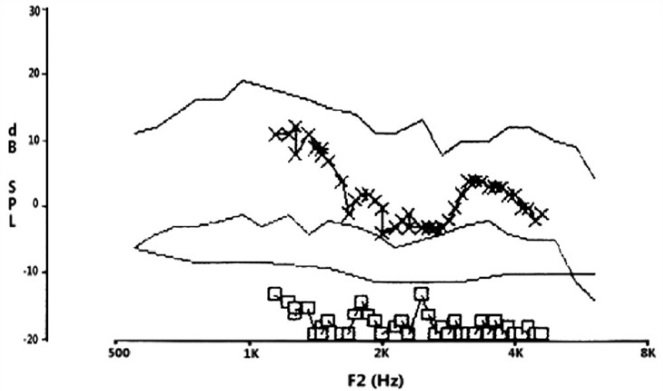
Figure 1: Normal Diagnostic DPOAE (DPgram)
Many audiology clinics have added OAE to the standard battery of tests that they perform on every ear/hearing patient. Since patient participation is not needed, the results are completely objective. The OAE findings should agree with the behavioral audiogram. If they do, then the clinician can conclude that the audiogram is accurate, and that the hearing loss, if present, is due to a cochlear hair cell deficit, provided there is no evidence of conductive pathology.
If the audiogram indicates a hearing loss, but the OAE and the pure tone audiogram do not agree, the patient may be malingering (faking a hearing loss) or there may be some retro-cochlear pathology causing the elevated hearing thresholds. DPOAEs have a very high sensitivity. They may indicate high frequency hair cell damage from ototoxic drugs or noise exposure before it is measurable on an audiogram. OAEs have also been shown to be helpful in identifying the frequency range of tinnitus in certain cases.
Virtually every expert in the field of audiology agrees that this OAE cross-check is a welcomed addition to the standard audiological test battery. The use of this cross-check between the audiogram and the OAE test results (DPgram) has proven valuable in numerous clinical studies. OAE testing is especially useful for the following applications:
-
Infant & Pediatric Hearing Screening
-
Identification of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
-
Identification of Retro-Cochlear Pathology (when it is not consistent with the audiogram)
-
Identification of Malingering
-
Indication Ototoxic Effects
-
Identification of Certain Types of Tinnitus
The OAE CPT codes are 95587 (limited) and 92588 (12-frequency diagnostic). There are both hand-held and PC-based DPOAE systems available today. Some of the hand-held devices can perform both the limited and the diagnostic OAE protocols, and the test results can be either sent to a computer, via the included software, to develop an electronic record or simply printed directly. Besides all of this, OAE has one of the best ROIs (return on investment) of any device used in an audiology practice.
Figure 2: Grason Stadler Corti OAE Device
OAE testing is indeed an asset for every ENT/audiology practice, and it should be considered a valuable component of every standard audiological test battery.